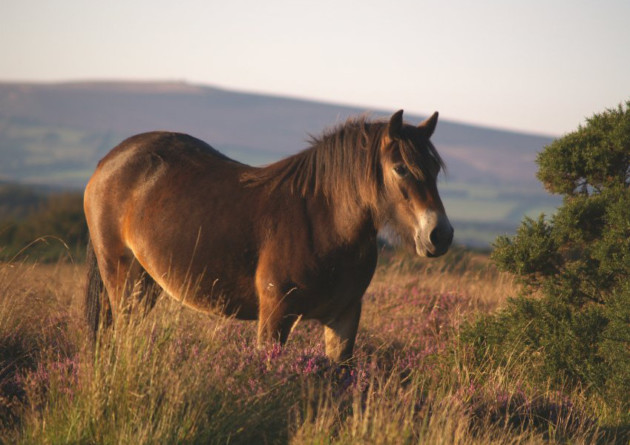
Exmoor ponies
Paul Bloomfield
Within the ancient coastal landscape of Exmoor National Park, the stars of the show are Britain’s oldest native ponies, which continue to roam freely, just as they have here for millennia.
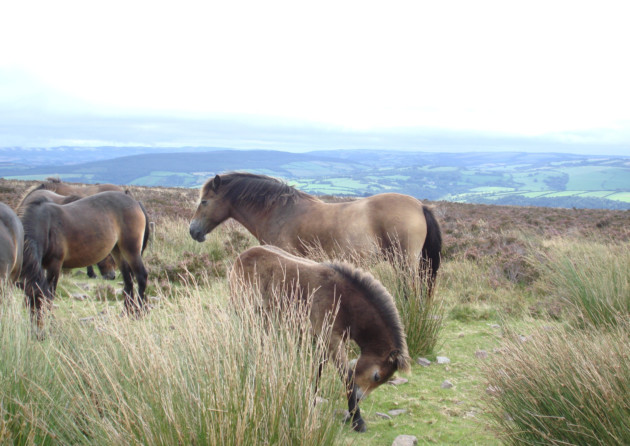

Exmoor ponies. Exmoor Pony Society
For a prehistoric animal encounter in modern Britain, head to Exmoor. Lace up your walking boots and stride out onto the dramatic heathland. Make for a wild, lonely spot: the slopes of Dunkery Beacon, perhaps – at 519m, Exmoor’s highest point – or Winsford Hill, ignoring its ancient Bronze Age burial barrows (they’re too recent for this moment).
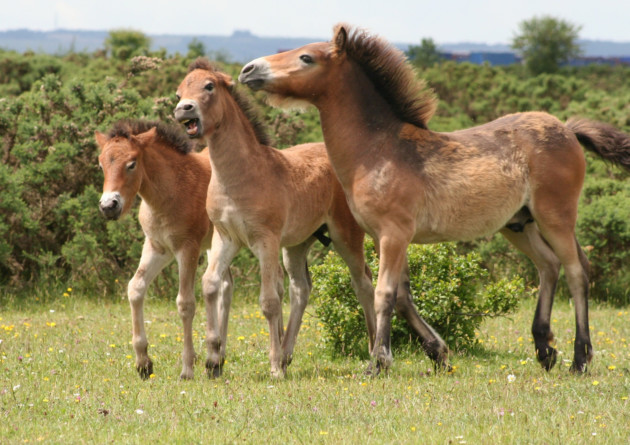

Foals on Greenham. Exmoor Pony Society/Phil Cottrell/Veronica Lilley
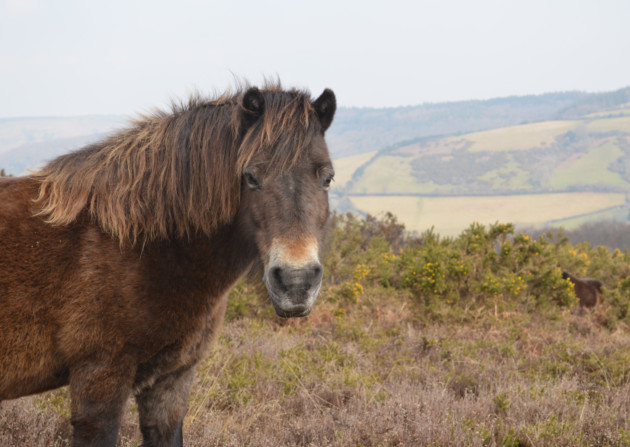

Out on Exmoor. Exmoor Pony Society
Now think like a Stone-Age hunter. Scan the heather and long, rough grass, and try to make out a sign – a long mane swaying in the breeze, a pale muzzle. A shape begins to emerge from the undergrowth: a pony, short and stocky, not quite like any horse you’ve laid eyes on before.
It’s a sight that our ancient ancestors would have witnessed when they arrived in the area that’s now the Somerset-Devon border. And meeting a free-living Exmoor pony is still an electrifying experience 10,000 years later, not least because they’re so rare. Only perhaps 4,000 survive around the world – about the same number as wild tigers and giant pandas – and a mere 500 or so mares, stallions and youngstock still live free on Exmoor. For this reason, they are classed as Endangered by the Rare Breeds Survival Trust, though the term ‘breed’ is slightly misleading. An expert from the Exmoor Pony Society suggests the word ‘race’ is more accurate, since there is no sign of human influence in its breeding – this pony remains as nature moulded it.
A cannon (leg) bone from a modern Exmoor animal has been compared with one found in Alaska and dated to about 30,000 years ago: they’re nigh identical. Similarly, the dental features of modern Exmoor ponies closely match those of prehistoric animals unearthed at sites across Europe. It’s been conjectured that this breed is virtually unchanged since the end of the last Ice Age, or even since wild ponies first arrived in Britain some 130,000 years ago; indeed, its colour and markings are similar to other ancient wild equines, such as Przewalski’s horse.
The irony is that this ancient, wild-looking native mammal isn’t actually wild. All of the pure-bred ponies on Exmoor are owned by hill farmers, and each belongs to one of 21 numbered herds, grazing designated areas (though on this largely unfenced moorland, most animals move around independently – hence the description ‘free-living’).
So how has the Exmoor pony remained unchanged for so long? Part of the answer is that it’s so perfectly adapted to this environment. A dun, bay or brown coat protects it from extreme conditions on the moor. Or should that be ‘coats’? In winter, each pony sports two layers: a short, woolly undercoat, like an insulating thermal vest, and a thick, greasy outer coat – a waterproof jacket, patterned to channel away rain. The long forelock and mane keep harsh rain, wind and snow off the neck, as well as deterring flies, and the low-slung, fanned tail also directs rain and snow from the body.
Its feet are dark (‘blue’) above and underneath, and very tough – Exmoor ponies are almost never shod. Its teeth are large and strongly rooted, for grazing the coarsest of plants. Its ears are small, to minimise heat loss, and eyes are protected by fleshy pads (sometimes described as ‘toad eyes’); these again keep out the elements, and may have offered protection from predators’ claws when such creatures still roamed the moors. It’s short (about 12 hands high), stocky and very strong, with a large heart and lungs.
Perhaps that’s why human interference hasn’t made much difference to the Exmoor pony: it’s already a perfect grazing machine for this tough environment, and any cross-breeding results in offspring that aren’t hardy enough to cope with the challenges of moorland winters.
Not that people haven’t used the ponies over the centuries, as Linzi Green, pony officer of the Moorland Mousie Trust, explains. “They were used by Iron Age people and Romans to pull carts,” she says. “If you watch a history documentary with a reconstruction of say, Boudicca’s battles, the chariots will be pulled by Exmoor ponies, because skeletal evidence shows they’re the closest in form to those early breeds.”
These animals were mentioned in the Domesday Book and, later, in medieval records when the moorland became enclosed and its ponies claimed by landowners. When the royal forest was sold by the crown in 1818, Sir Thomas Acland, last warden of the forest, took 30 animals to run the hills above Porlock – ponies branded with the distinctive anchor mark since 1797, and ancestors of the biggest herd on the moor today. More were sold in a dispersal sale, forming the basis of other modern herds.
Horsemeat is no longer popular in Britain – but it was, and in hard times poaching almost spelled the end for the breed. “During the Second World War, most of the Anchor Herd – in fact, most ponies on the moor – were rustled for meat,” explains Emma Wallace, who owns the herd today. It’s even believed that the ponies were used for target practice. “In total only about 50 pure-bred ponies survived, with a mere eight mares remaining in our herd.”
Fortunately, supporters were on hand to protect the remaining ponies. Many herd owners worked hard on the recovery, most driven not by commercial motives – the market for these animals is small – but by passion for the breed. “They’re part of our heritage,” Emma says, “and unique, physically and in character. They’re very… shall we say, spirited!”
The Anchor Herd, today numbering about 100, has been in David Wallace’s family since the first half of the 20th century, and he and Emma are committed to the breed’s conservation and welfare. “When we inherited the herd, we had 60 or 70 ponies descended from the eight foundation mares that survived the war,” she explained. “But the bloodlines weren’t evenly represented, so we had a lot of work to do to ensure the continuation of the lines.”
These challenges – maintaining genetic diversity and the survival of the various bloodlines – are two of the major issues facing the Exmoor Pony Society. Founded in 1921 to encourage the breeding of pure stock, in 1963 it produced the first stud book. “Though the pony is now well established worldwide, on the moor the situation is still perilous,” says the Society’s Sue McGeever. “Finding homes for the 100 or so foals born each year is the biggest concern, but we also have problems with ponies just being dumped on the moor – many crossbreeds that could mate with the pure-bred animals.”
To counter these difficulties, each autumn all of the free-living ponies are rounded up and inspected by the Exmoor Pony Society. Newborn foals are rigorously inspected to ensure they meet the standards for the breed: for example, feet must be black or slate grey, the coat must have no white hairs, and the muzzle must be pale or ‘mealy’. DNA samples are taken to verify parentage, and pure-bred foals micro-chipped; those remaining on the moor are also branded, if requested, to identify the herd and pony number.
And what happens to those offspring? Originally used for ploughing, sheep-gathering or collecting the groceries, moorland ponies have always been brought off the moor to play a domestic role. Nowadays, herd owners also sell their foals to individual owners to become family ponies whether it be for hacking, showing, driving or endurance riding. That said, there’s grazing space on the moor for only a limited number, and excess youngsters have been sent for slaughter, some to feed carnivores in local zoos. Today, the Moorland Mousie Trust works with the herd owners and takes as many foals as possible. Many make excellent riding ponies for teenagers and lightweight adults and can take part in all pony and riding club activities; the breed is becoming increasingly popular at shows. Many, though, are left to do what they do best: eat!
On Exmoor the ponies play a vital role in managing the habitat. “In autumn particularly, when the tasty, soft new shoots aren’t abundant, they graze rough pasture,” Emma explains. “They munch the coarsest plants, allowing species such as heather to flourish.” For this reason, Exmoors are lent across Britain for conservation grazing. “You can see them in Snellsmore and Greenham Commons in Berkshire, the Sussex Downs, Cumbrian hills – even in Scotland,” Sue reports. Ponies are also sent around the world for breeding.
Visitors to the Exmoor Pony Centre near Dulverton can see both young foals and older ponies, and join rides in the yard or on the moor; the Exmoor Pony Festival in August offers another great opportunity to meet one up close. But an Exmoor pony never looks quite as wonderful – as right – as it does in its natural habitat. Good places to spot them are Winsford Hill (the Anchor Herd), West Anstey, Brendon and Twitchen Commons, Withypool and Countisbury. You’ll need those Stone-Age tracking skills, though. “I quite like the fact that on Exmoor it’s not so easy to see the ponies as in other places,” says Linzi. “They’re a bit more mysterious, and it helps you to enjoy the environment more.”
It’s certainly worth the effort. “There’s nothing quite like seeing the ponies come in off Winsford Hill or Withypool in the annual autumn round-up,” smiles Sue. “Best is the spectacle of ponies on Dunkery Beacon or Porlock Hill, with the sea sparkling in the background. It’s simply awesome.” n
For more information on the Exmoor Pony Centre call 01398 323 093 or visit www.moorlandmousietrust.org.uk