Hidden Tudor architecture in London
Away from the popular destinations, the capital’s lesser-known Tudor palaces and houses paint a more vivid portrait of this fascinating era, as Nicola Rayner explains
In 1578, a French visitor to the UK’s capital wrote: “Rumour of the greatness, prosperity, singularities and splendours of London fly and run to the ends of the whole world.” It wasn’t always so: London under the Tudors – from 1485 when Henry VII defeated Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field until the passing of Queen Elizabeth I in 1603 – changed enormously. During this period, the capital was a city on its way up in the world, as its population quadrupled from around 50,000 people in 1500 to 200,000 in 1600.
For centuries, the walled City of London in the east and Westminster in the west had been geographically distinct, but the new Tudor age would unite these two disparate settlements, creating the beginnings of the city as we know today – a hustling, bustling place with a terrible traffic problem. With the addition of Hackney coaches to the “cars, drays and carts”, the problem grew worse, with John Stow, the historian and antiquarian whose monument can be found at St Andrew Undershaft, moaning that “the world runs on wheels”.
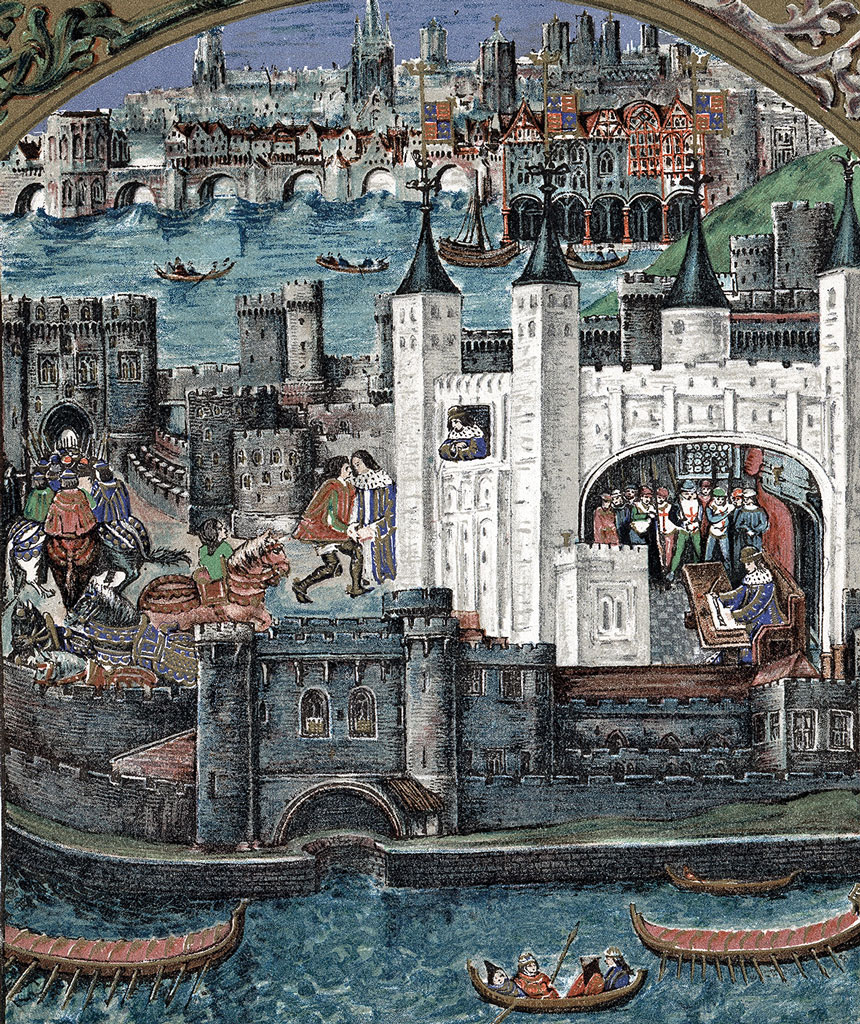
London Bridge, home to around 200 buildings, saw the worst congestion. It was the only bridge over the River Thames in central London at that time and crossing it could take more than an hour – for many it was more convenient to cross via small passenger boats known as ‘wherries’. Today, for a taste of Tudor London, a walk along the Thames is not a bad place to start with modern replicas of Shakespeare’s Globe and Sir Francis Drake’s Golden Hinde calling to mind some of the most famous people of that era.
READ MORE: The Tower of London
The most covetable land during the Tudor era could be found along the Thames – a fact that did not escape the attention of the avaricious King Henry VIII. In what has been called the biggest land grab in British history, the Dissolution of the Monasteries between 1536 and 1541 saw grand houses along the river seized from bishops and given to the king’s nearest and dearest. Durham House, for example, was claimed from the Bishop of Durham and given to Anne Boleyn.

In East London’s Hackney, one beneficiary of the Tudor king’s favour can still be explored today. Sutton House was built in the 1530s as a country house for Henry VIII’s courtier Sir Ralph Sadler (or Sadleir), who started out as a protégé of the statesman Thomas Cromwell. Sadler joined Cromwell’s household at the age of 14, where he learned Latin and much else besides that would, no doubt, later benefit his political career.

Known originally as “the bryk place”, Sutton House is a rare example of a Tudor redbrick that later became home to a succession of sea captains, Huguenot silk-weavers, Victorian schoolmistresses and Edwardian clergy. Although the front was altered in the Georgian period, Tudor treasures abound inside, including the oak-panelled Great Chamber filled with portraits, and a rare linenfold room, so called because the wood is carved to resemble linen.
Staying in east London, Eastbury Manor House is another National Trust-run property that sprang from the religious reformation. Built in the 1570s by Clement Sisley, a wealthy merchant who bought the land after the closure of Barking Abbey, it was probably the first brick-built building in the area at that time. The house’s glass windows and soaring chimneys, which survive today, were a bold advertisement for the wealth of the owner.
Other treasures at Eastbury Manor House include an original spiral oak staircase in the turret, exposed timbers in the attic, and a walled garden with “secret bee boles” – wall recesses designed to house a beehive. Local legend has it that the occupants were rather less loyal to the monarchy as the house rumoured to be where Guy Fawkes’ Gunpowder Plot to kill King James I during the State Opening of Parliament in 1605 was first conceived.
A far more accommodating home for royalty can be found at Eltham Palace in Greenwich. Though best known today for its art deco extension, it was once one of the grandest royal residencies in the country, serving as a royal nursery for Henry VIII and his sisters, Margaret and Mary. The famous scholar Erasmus gave us an early glimpse of the future monarch during a trip to Eltham Palace in 1499, during which he was presented to the royal children in Edward IV’s Great Hall: “In the midst stood Prince Henry, now nine years old, and having already something of royalty in his demeanour, in which there was a certain dignity combined with singular courtesy.”
Today, the same Great Hall remains one of the highlights at Eltham, now managed by English Heritage, where the glorious hammer-beam roof dates from the 1470s – though it was dismantled and reassembled prior to the First World War. In fact, Henry VIII was the last monarch to significantly invest in Eltham, laying out a tiltyard (a courtyard for jousting) to the east of the palace in 1517 and, later, new royal lodgings and a brick-built chapel, which today is buried under the lawn. Yet the rival attractions of Whitehall, Hampton Court and Greenwich meant the palace later fell out of favour, and by the 17th century James I found the palace “farre in decay” [sic].
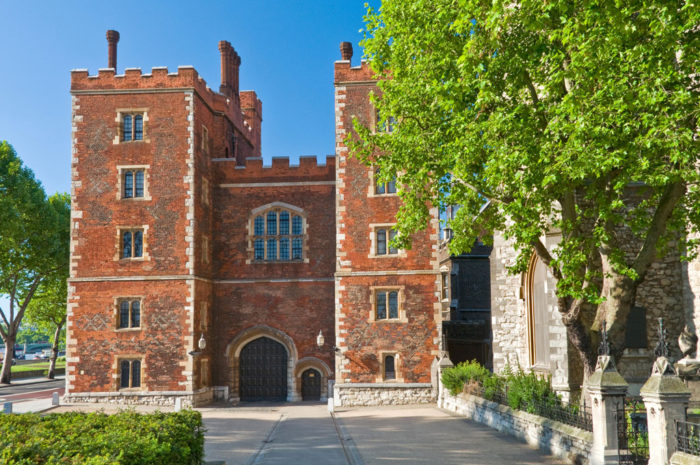
Another witness to the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, Lambeth Palace, the official London residence of the Archbishop of Canterbury since the 13th century, lost its Great Hall during the English Civil War, while other buildings followed in the 19th century. However, Tudor architecture lovers can still enjoy the late 15th-century Morton’s Tower gatehouse, while Lollard’s Tower, the Guard Room, the chapel and the crypt all date from prior to this time and represent what was the Tudor heart of the palace. If walls could talk, these sturdy structures would have a few secrets to share.
It was at “a certain well-known high gallery in the manor of Lambeth” that Henry VIII’s controversial marriage to Anne Boleyn was declared valid in 1553 – a fact that might have stung a former visitor, Henry VIII’s first wife Katherine of Aragon, who stayed at Lambeth as a 15-year-old. Today the library at the palace is home to two volumes of papers relating to Henry VIII’s divorce proceedings against his first wife, as well as a contemporary copy of the warrant for the execution of Mary, Queen of Scots.
One rural treasure worth venturing further out of the city for is Queen Elizabeth’s Hunting Lodge – a remarkable example of a surviving timber-framed Tudor construction standing on the edge of Epping Forest to the northeast of London. Although it was built in 1543 on the orders of Henry VIII to view the deer chase at Chingford, it was renovated in 1589 for Elizabeth I. Functioning today as a museum, the lodge focuses on Tudor food on the ground floor and fashion on the first. The second floor offers atmospheric views, where you can almost hear the thrum of the horses’ hooves on a hunt day and admire the Tudor timber roof construction.
Another little-known gem is Whitehall Historic House in the South London village of Cheam. Built in the early 1500s, the timber-framed structure is a rare surviving example of Tudor domestic architecture, possibly once a meeting or council house.
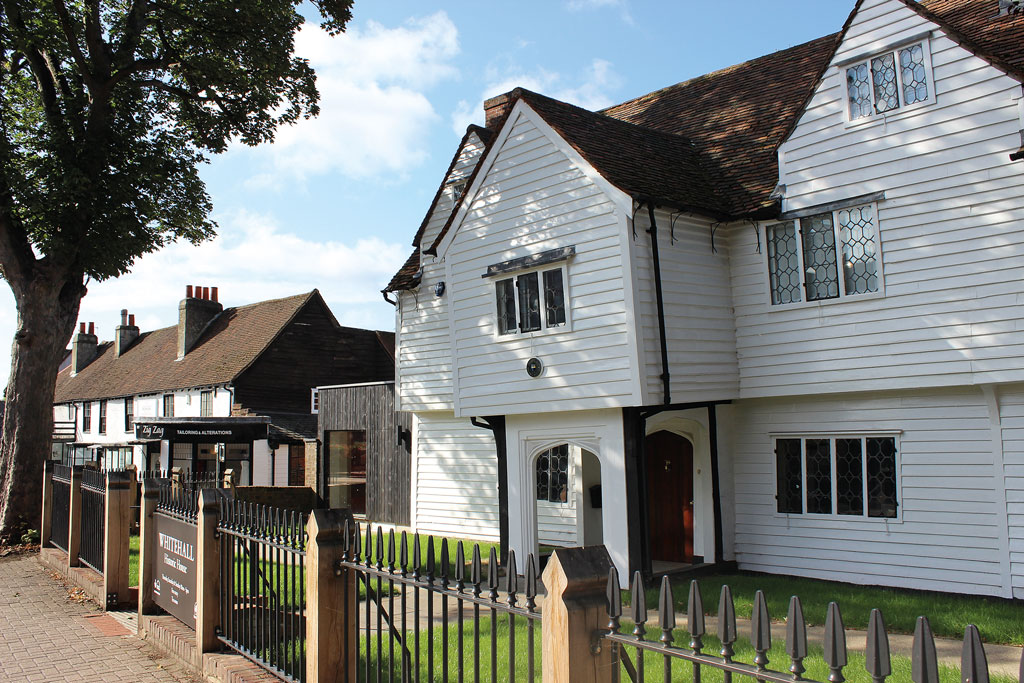

Recently restored, the interior now houses a museum dedicated to local life through the ages, including a display dedicated to the nearby Nonsuch Palace, a grand folly of Henry VIII that remained incomplete when he died in 1547 and would eventually be pulled down less than 150 years later. Whitehall’s weatherboard cladding was added in the 18th century and covers the original wattle-and-daub, timber building.
Unfortunately, such constructions have their downside – as would become all too clear in the subsequent Stuart era. In a city of closely-packed timber buildings covered in flammable pitch, the Great Fire of London in 1666 was an accident waiting to happen, sadly wiping out whole swathes of the city as the Tudors would have known it, including Old St Paul’s Cathedral.
A rare Tudor survivor of both that catastrophe and the blitz of the Second World War, St Andrew Undershaft stands at the historic centre of the old city. A church has stood on the site since the 12th century, but the Church of England building you see today was completed in 1532. Inside you will find a shrine to former parishioner and Tudor historian, John Stow, author of Survey of London, a ward by ward tour of the city and its customs. His statue holds a real quill pen that is replaced by the Worshipful Company of Merchant Taylors, to which Stow belonged, in a special ceremony every three years – the next is due to take place in 2020.
St Andrew Undershaft’s unusual name comes from the maypole that was traditionally erected opposite it every year, but today it most often appears in photographs in the shadow of the ‘Gherkin’ (Norman Foster’s 30 St Mary Axe) instead – an image that highlights how remarkable its survival is in our much-changed world.
READ MORE: British Monarchy: The Tudors, 1485–1603