The curse of Oliver Cromwell: Our most controversial leader?
Was Oliver Cromwell really our most controversial leader? Alexander Larman reassesses Britain’s short-lived attempt at being governed as a republic
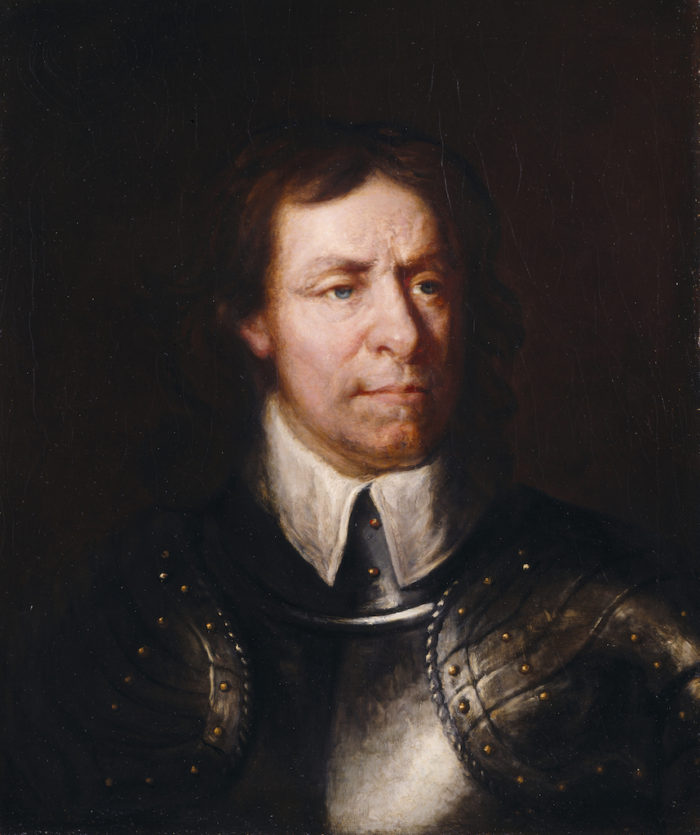
In the history of Britain’s rulers, there is an uncomfortable 11-year gap between the reigns of Charles I, which ended in 1649, and Charles II, which began in 1660. The reason for that gap – and for the discomfort – is that Charles I remains the only English king to have been executed for high treason, a controversial event at the time, and ever since. The man responsible was the Parliamentarian general Oliver Cromwell, who later founded the first (and, to date, last) English republic and established himself as Lord Protector of England.
Today, Cromwell remains the most polarising of figures in British history. His defenders applaud him as a just and righteous man, who attempted to rebuild his country on moral and egalitarian lines. His detractors, meanwhile, condemn him as a sadistic and power-crazed totalitarian who created an aggressive political fundamentalist group in 17th-century England. But is either of these an accurate account of the country’s sole non-regal ruler, or is the truth more complex?
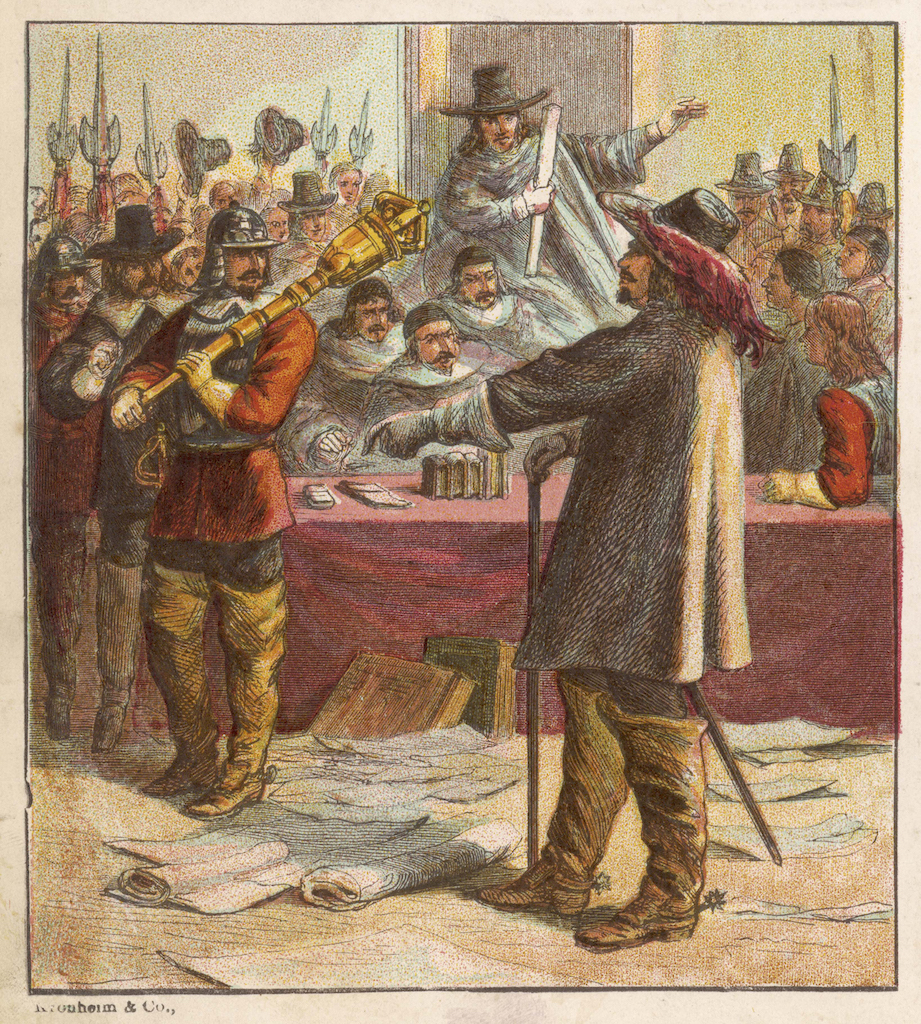

By the time of Charles I’s execution on 30 January 1649, Cromwell had transformed himself from a low-profile Cambridgeshire MP into one of the principal commanders of the New Model Army (the Parliamentarian forces that had routed the king) and a key signatory of Charles’s death warrant.
While many others had resisted the apparently sacrilegious decision to execute the monarch, Cromwell believed that the unprecedented and dramatic action was necessary to end the Civil War which had bitterly divided the country, and thereby establish the so-called “Commonwealth of England”. Many were grateful for the end to conflict; it resulted in 100,000 deaths – a vast number in a country with around six million inhabitants.
The foundation of the Commonwealth was a remarkable event in English history. It was the precursor to the Protectorate of 1653 and testament to Cromwell’s self-belief. It was a new kind of country that he had in mind, one based on a rigid, almost fanatical, belief in religion, and one that cast away the luxurious trappings of Charles I’s rule and court in favour of a far more ascetic and strict way of life.
There was no tolerance for any national religious belief other than Puritanism. The Anglican faith was all but banned, both by forbidding its clergy to preach and also by the closure and desecration of its churches. Catholicism was similarly outlawed, its practitioners persecuted, and Cromwell began to think of England’s rebellious neighbour, Ireland, with the zeal of a king embarking upon a righteous crusade.
Read more:
Best places to visit in Northumberland: top attractions, and places to stay, eat and drink
Nominate your British heroes: Who do you think has shaped our nation?