Midsummer celebrations in Britain
Adrian Mourby looks at midsummer celebrations in Britain and how the longest days of summer have are rooted in ancient tradition and have been celebration in Britain for millenia
This year 21 June marks the summer solstice in the northern hemisphere, when the earth is at its maximum tilt towards the sun and days are at their longest.
We call it ‘midsummer’ in Britain and while that is chronologically correct – the sun will not be as high again in the sky for another 12 months – our damp maritime climate tends to make this date feel like the beginning of summer rather than its midpoint.
However, from late June onwards Britain warms up. We take boats out on lakes and rivers, we opt for shorts and sundresses regardless of the weather forecast, and we picnic at the seaside even if, at any moment, rain clouds may send us scurrying back to our cars.
The longest day and all the subsequent joys of summer are important points in the British psyche. Year after year we soldier on through dark, wet winters, focusing on summer’s promise of warmth and easy living as our reward and it’s no new trend.
Across Britain, over millennia many traditions have become associated with Midsummer’s Eve and Midsummer’s Day, which traditionally take place a few days after the summer solstice.

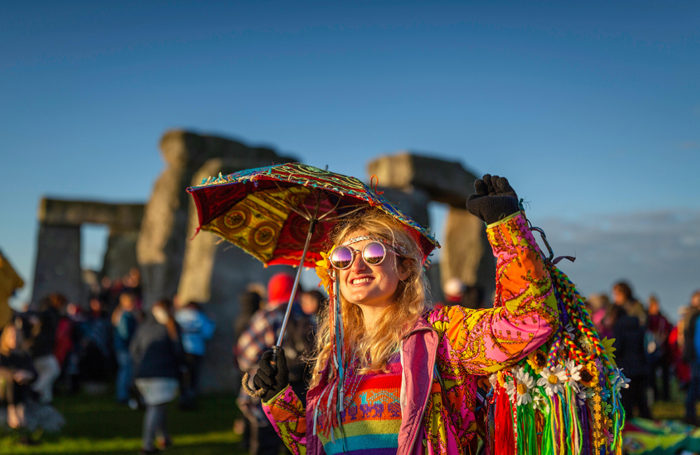
Midsummer Celebrations at Stonehenge
Most commonly, people aim to be somewhere that they can watch the sun rise on the summer solstice – which is usually around 5am. Stonehenge is one of the most famous sites in the world for this yearly vigil. It was built 5,000 years ago, possibly as a place of healing as well as a celestial observatory, though historians are still unsure. Stonehenge’s alignments certainly fit with the rising sun of the summer solstice and there are also some lesser-known stone circles where the solstice sunrise can be observed.
Read more about Stonehenge, here.
For example, in Devon, three wonderfully-named sites: Hingston Hill, Drizzlecombe, and Merrivale are all popular Dartmoor meeting points at dawn, though none can match Stonehenge’s crowds – in 2019, 10,000 revellers watched the sun rise at the iconic stone circle. Bonfires are another tradition associated with midsummer in Britain. Considering this festival takes place at the brightest and warmest time of the year, it seems ironic that so many celebrations are based around flames.

Midsummer Celebrations around Britain
Leaping over bonfires was – and still is – a popular pastime on Midsummer’s Eve in some parts of Britain, especially Yorkshire. Traditionally, the highest leap indicated the height that wheat might grow that summer.
Flaming torches are frequently carried in midsummer processions, and if fire were not spectacular enough, when gunpowder reached British shores, places like Trencom Hill in West Cornwall cut ‘midsummer holes’ into the rock. Every summer solstice these would be filled with gunpowder and plugged with clay and then detonated as darkness approached on Midsummer’s Eve.
A pre-Christian explanation for all these flames ran that at such a powerful time of the year – when the sun was never stronger – the veil between this world and all others was very thin indeed, so evil spirits were emboldened to walk the Northern Hemisphere.
Also, at this time, old-year fairies might steal babies and replace them with changeling replicas who, on closer inspection, looked like little old men.
So, fire was a good way of deterring demons. Another precaution was picking special flowers and herbs that the harvester could weave into protective garlands.
Plants plucked on Midsummer’s Eve had special potency. St John’s Wort with its blood-red sap if lain to dry on a window ledge could keep the house free of evil spirits, fire, and thunderbolts. Worn around the neck, it even guarded against mental illness. Vervain, trefoil and rose were also considered efficacious and worth picking, as was – ironically – the abortifacient, rue.
Read more: