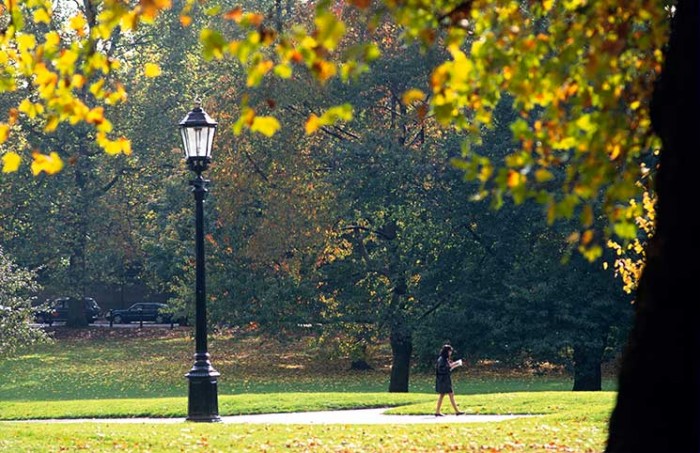
How well do you know London’s royal parks?
London’s Royal Parks include Regent’s Park, Green Park, St James’s Park, Richmond Park, Kensington Gardens, Hyde Park, Greenwich Park and Bushy Park. They make up 5,000 of the capital’s greenest acres. We look at some of the most popular
The royal parks have been owned by the monarchy since the 15th century. Although public spaces today, they were not always so welcoming and were used primarily by the royal household in the 15th century for leisure pursuits such as hunting. King Henry VIII transformed St James’s Park, the oldest of the eight, from a marshland into a deer park and built St James’s Palace. His daughter Elizabeth I later staged great fetes in the park, and successors James I and Charles II are credited with transforming the grounds into more formal landscapes, which were later remodelled by John Nash. Today, the park provides a gateway to two other of London’s great palaces – Buckingham and Westminster.
Despite their wide open spaces and vast expanses of grass, these green spaces are more than manicured lawns. As the sites of much needed vegetable plots during the Second World War, St James’s Park, Kensington Gardens and The Regent’s Park still contain allotments that are tended by green-fingered locals.
Attractions and facilities vary throughout. Over in Bushy Park, north of Hampton Court Palace, visitors can follow heritage audio trails; in Greenwich Park signs point the way to the site of Roman remains; and wild deer are a common sight in the national nature reserve of Richmond Park. Dotted throughout each of the eight parks are built and natural relics, ranging from fossilised trees and Anglo-Saxon burial mounds to modern memorials. Together, these restful parks make a vital contribution to life in the capital.
Hyde Park
More than seven million people visit this park each year, exploring 350 acres of paths. The park is popular with cyclists and horse riders on designated paths, as well as swimmers and boaters on the Serpentine. With an Underground station on all four corners, the park is easy to get to. Today, tai chi is practised between the trees by early morning visitors, and picnickers come to find shady spots on warm afternoons. It’s a far cry from the days when Henry VIII would race across on horseback in pursuit of deer and wild boar. The king commandeered the park from Westminster Abbey in 1536, turning it into a playground where he could indulge in the thrill of the chase.
Life changed with the coronation of Charles I who decided to open the park to the public in 1637, introducing a ring path around which the fashionable gentry would circulate. During the political instability of the Civil War, parliamentary troops built forts and dug earthworks to defend their position – signs of which are still visible today. Following the restoration in 1660, the park returned to a peaceful royal haven once again under Charles II, who put a perimeter brick wall in place and stepped up the park’s role as a centre of spectacle, pomp and ceremony.
Successive royalty made alterations to the access, notably William III who installed oil lamps along the route from Hyde Park Corner to Kensington Palace when his journeys after dark became too hazardous. Queen Caroline added the Serpentine feature in the 1730s, and 200 years later a lido was added, which is still in use during the summer.
Once a venue for national celebrations including the Great Exhibition of 1851, and home of the political sounding stage Speaker’s Corner since 1872, the park is steeped in history, but it can be easy to overlook its most simple attractions. The park’s flora and fauna is surprisingly diverse, with the park providing home to a variety butterflies and birds such as long-tailed tits and great crested grebes. Recent sightings include a black swan, buzzards and Egyptian geese. A specially created meadow area reflects how the entire park once looked during its days as a wild hunting ground, and is prime habitat for bees and insects.
Memorials provide an alternative attraction. The Diana, Princess of Wales Memorial Walk is a seven-mile trail incorporating St James’s Park, Green Park, Hyde Park and Kensington Gardens. Along the way, walkers can see prominent buildings associated with the life of the ‘People’s Princess’.
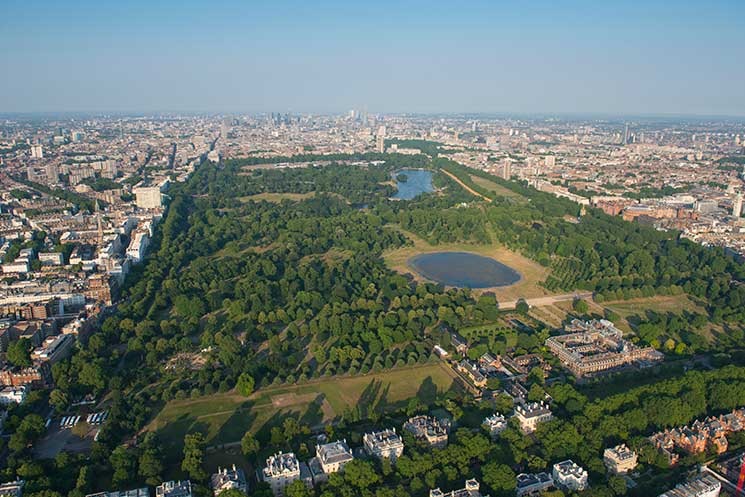

Kensington Gardens
Three royal women are responsible for shaping the park seen today, which originally formed part of King Henry VIII’s hunting ground. The first was Queen Mary who introduced formal flower beds and box hedges in the Dutch fashion to reflect those found in Holland, the native home of her husband, King William. When Anne came to the throne in 1702, she extended the borders of the garden, taking 30 acres from Hyde Park to transform into a quintessential English garden, also adding an orangery. Yet of all the queens, it was Caroline whose efforts can best be appreciated today. Not satisfied with the size of the grounds she took a further 300 acres from Hyde Park and employed Charles Bridgeman to create a landscape which would place the Palace as the central focus. Long, tree-lined avenues branching out from around a pond at the front of the palace offered tantalising glimpses of the building from different angles. The damming of a stream gave the illusion of a natural lake known as the Long Water, and a clever landscape device known as a ‘ha-ha’ fooled the eye into seeing a landscape with no borders, when in fact a ditch separated Kensington from Hyde Park.
The gardens were opened to ‘respectably dressed’ members of the public on Saturdays and for a time Kensington Gardens were the place to see and be seen. On Queen Victoria’s accession in 1837 the royal court was moved to Buckingham Palace, and the public gaze shifted accordingly. Today the gardens are a place of repose and remembrance. Sculpture adorns the green, including Henry Moore’s six-metre high Arch on the north bank of the Long Water, while the Italian Gardens feature a rich assembly of marble fountains, statues and intricately carved urns. Memorials stand here of various commended citizens, including the Albert memorial, and statues of Edward Jenner, John Hanning Speke and one of fiction’s best-loved figures, Peter Pan. Many of the royal parks have featured in major films, and Kensington is no exception. The Peter Pan connection was never more relevant than in the production of Finding Neverland in 2004. That same year the gardens were the star attraction once more in Bridget Jones: The Edge of Reason when two love rivals start a fist fight in the fountain of the Italian Garden. The park is also home to the Diana Memorial Playground, enjoyed by 750,000 youngsters each year.
Regent’s Park
Known as the ‘jewel in the Crown’, Regent’s Park came to royal ownership in 1538 when King Henry VIII seized the land from the Abbess of Barking to create a sizeable hunting chase of 554 acres. The park originally formed part of the dense forest of Middlesex, and was known as Marylebone Park after the nearby manor. As a playground for the king and visiting dignitaries the park remained relatively unscathed for over a century but the Civil War changed that. Hundreds of trees were felled under Oliver Cromwell to pay off war debts, clearing the land for a post-Restoration opportunity of leasing the parkland to tenant farmers. More money for the royal coffers was made in 1811 when the Crown earmarked some of the park for a building project fit for the high ideals of the new Prince Regent.
Renamed The Regent’s Park, ambitious plans were drawn up by architect John Nash. His vision was to design a circular park with a royal home at the heart of it, which would be connected by road to St James’s Palace. Exclusive villas and terraces were factored in to pay for the project, the potential new homes for the capital’s wealthiest citizens. Nash’s bold scheme was, however, only partly completed as the Prince focused instead on improving Buckingham Palace. Of the 56 planned, just eight villas were built in the park (of which only two now survive), as well as a processional route to St James’s Palace (which later became Regent’s Street).
The gentry moved in, as did the Zoological Society, The Royal Botanic Society and The Royal Toxophilite Society, each of which helped to cultivate their own patch of the park into attractive gardens. Gates opened to the general public from 1835 during the reign of William IV and summertime brought the Open Air Theatre to perform in front of crowds, still a regular event.
Today, the pockets of Regent’s Park are full of life: a designated community wildlife garden has helped encouraged flora and fauna and doubles as a centre for public art; the allotment garden is a hive of activity for all those interested in learning about and growing vegetables; and sports from softball to rugby can be played by those interested in more than just a gentle stroll.
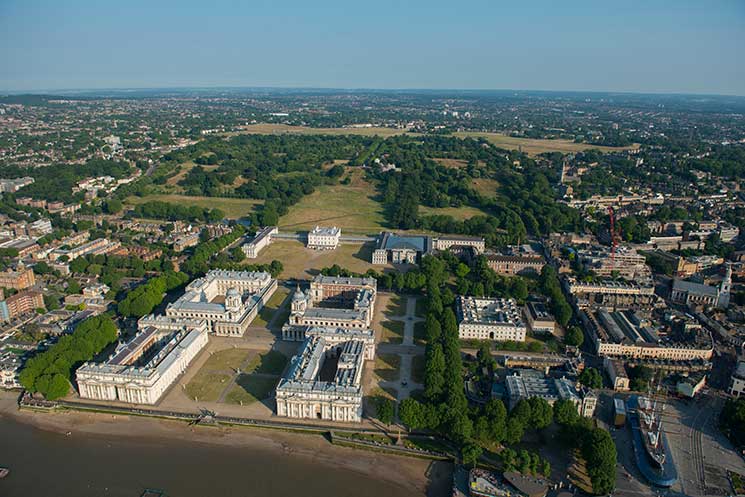

Greenwich Park
Synonymous with royalty since the time of Henry V, this 183-acre park is the oldest enclosed royal park and has much to its credit, including incredible views across the Thames towards the City and a World Heritage Site neighbourhood of historic buildings. Greenwich is a visitor attraction in its own right comprising the Old Royal Observatory, Old Royal Naval College, National Maritime Museum and the Inigo Jones-designed Queen’s House, a former residence of Queen Anne. Ensuing monarchs have stamped their mark on this prime landscape including Henry VII who built Greenwich Palace (on which the Old Royal Naval College now stands). Henry VIII was born there in 1491, as were his daughters Mary I and Elizabeth I. Charles II’s interest in science led to the Christopher Wren-built Royal Observatory, which now forms part of the National Maritime Museum.
Though the park is enjoyed by many thousands of visitors, its ancient history can be easily overlooked. With a hilltop position the area was the preferred choice for early settlers who liked the safety it offered from lowland threat. Roman finds excavated during routine works in 1902 were connected to the site of a Romano-Celtic temple. Roman coins were unearthed, as well as pottery and three different types of floor surface. In 1999 Channel 4’s Time Team crews undertook a three-day dig; their findings have provided further evidence of what was once an extensive temple complex. Although layered in history the park remains ever present. For the London 2012 Olympics it provided an iconic stage for the equestrian Cross Country event, with fences positioned on the hillside to frame the cityscape.
From there, with the city in the distance and a little of the countryside beneath the feet, park visitors have the best of both worlds. As a Grade I-listed landscape and a Site of Metropolitan Importance for Nature Conservation, Greenwich Park is both historic landscape and wildlife haven. Henry VIII’s red and fallow deer may no longer roam the entire park, but they can still be viewed from special vantage points in a smaller area known as The Wilderness. This undisturbed sanctuary is dotted with ancient woodland and makes an excellent habitat for insects and small mammals. Elsewhere, on Croom’s Hill the ground is carpeted with fine grasses and wild flowers, attracting displays of butterflies and bees in the summer. It is a place to picnic, to enjoy refreshments in the Pavilion Tea House, and contemplate the landscape’s rich tapestry.
For more information on the royal parks, including events information and walking trails, call 0300 061 2000 or visit www.royalparks.org.uk
Words: Vicky Sartain